Flyback diodes, also known as freewheeling diodes or snubber diodes, are essential components in electrical circuits, particularly in circuits containing inductive loads such as motors, solenoids, and relays. They serve to protect sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes generated when an inductive load is suddenly switched off.
What is a Flyback Diode?
A flyback diode is a diode connected across an inductive load in such a way that it provides a path for the inductive current to circulate when the supply voltage is switched off. When an inductive load is switched off, it generates a voltage spike due to the collapse of the magnetic field around it. This voltage spike can damage electronic components in the circuit. The flyback diode provides a safe path for this current to circulate, preventing damage.
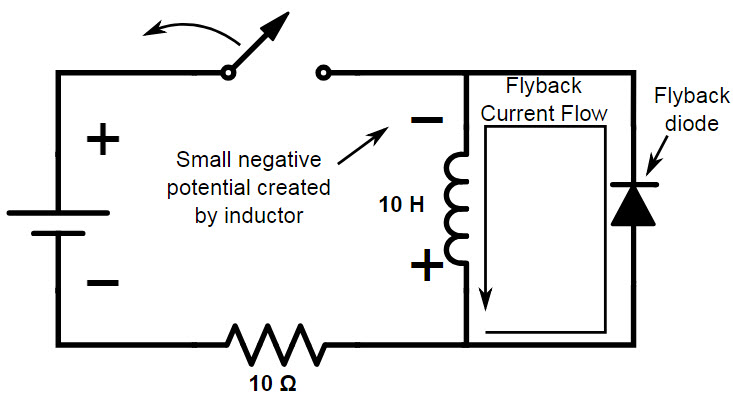
How Does a Flyback Diode Work?
When the current through an inductive load is interrupted, the energy stored in the inductor's magnetic field needs to go somewhere. Without a flyback diode, this energy can cause a voltage spike, potentially damaging other components in the circuit. However, by placing a diode across the inductive load in reverse bias, the diode becomes forward biased when the supply voltage is switched off. This allows the inductive current to circulate through the diode in a loop until it dissipates naturally, thus protecting the rest of the circuit.
Selection of Flyback Diode
Choosing the right flyback diode is crucial for effective protection of the circuit. Here are some factors to consider:
-
Reverse Voltage Rating: Ensure that the diode's reverse voltage rating is higher than the maximum voltage expected across the inductive load.
-
Forward Current Rating: The diode should be able to handle the maximum current expected to flow through it during the flyback period.
-
Recovery Time: The diode should have a fast recovery time to minimize the time it takes for the inductive current to circulate and dissipate.
-
Package Type: Select a package type that suits the application and facilitates easy mounting on the PCB.
Installation of Flyback Diode
Installing a flyback diode is relatively straightforward:
- Identify the terminals of the inductive load.
- Connect the cathode (marked side) of the flyback diode to the positive terminal of the load.
- Connect the anode of the diode to the negative terminal of the load.
Ensure the diode is mounted securely and that its leads are adequately soldered to prevent any intermittent connections.
Applications of Flyback Diodes
Flyback diodes find applications in various circuits where inductive loads are present. Some common applications include:
-
Motor Control Circuits: To protect the motor driver circuitry from voltage spikes generated during motor deceleration.
-
Relay Driver Circuits: To protect the control circuitry from voltage spikes generated during relay switch-off.
-
Solenoid Driver Circuits: To prevent damage to electronic components when solenoids are turned off.
Conclusion
Flyback diodes are essential components in circuits containing inductive loads. By providing a path for the inductive current to circulate when the load is switched off, they protect sensitive electronic components from damage due to voltage spikes. Proper selection and installation of flyback diodes are crucial for ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic circuits.
Facts Checked by Hugh Johnson
Hugh Johnson stands tall in the realms of both the Integrated Circuits (ic Chips) industry and the electronic parts industry, earning acclaim as an esteemed expert in these fields. With an extensive background steeped in semiconductor technology, Hugh's expertise transcends chip design and fabrication, encompassing a profound understanding of electronic components' intricate functionalities and applications. His seasoned knowledge spans diverse facets, from microchip architecture and fabrication techniques to the broader landscape of electronic parts utilized across industries.









