What is a Full Bridge Controlled Rectifier?
A Full Bridge Controlled Rectifier is a critical component in power electronics, designed to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) with precision and efficiency. This advanced rectification system utilizes four diodes in a bridge configuration and is often employed in various applications where controlled and reliable DC power is essential. Helpful resource: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/single-phase-rectification.html#:~:text=Single%20phase%20fully%2Dcontrolled%20bridge,rectifier%20with%20thyristors%20as%20shown.
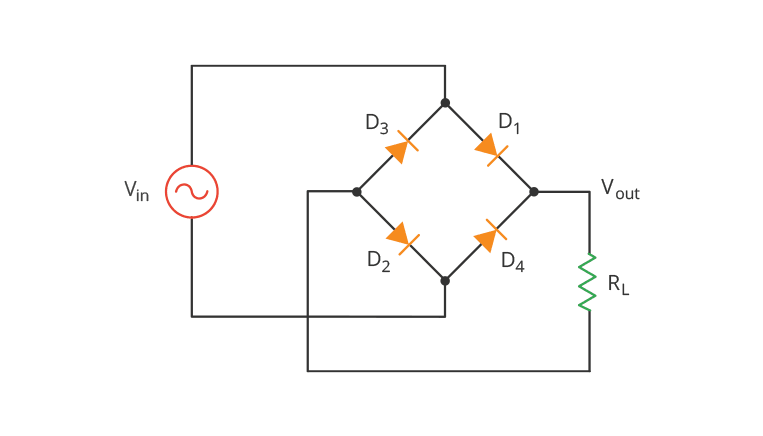
What Does a Full Bridge Rectifier Do?
The primary function of a Full Bridge Rectifier is to convert AC power into DC power by rectifying the input waveform. In the full bridge configuration, two diodes conduct during each half-cycle of the AC waveform, ensuring a continuous flow of current in the same direction. This process results in a smoother and more stable DC output, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic devices and applications. Helpful resource: https://www.analog.com/en/design-center/glossary/full-bridge-rectifier.html#:~:text=A%20rectifier%20converts%20an%20AC,rectifier%20provides%20full%2Dwave%20rectification.
Does a Full Bridge Rectifier Convert AC to DC?
Yes, a Full Bridge Rectifier converts AC to DC. Its ingenious design allows it to rectify the alternating current, ensuring that the output is a consistent and unidirectional flow of electrical energy. This conversion is vital for powering electronic devices, as many appliances and gadgets rely on a steady DC power supply for optimal performance. Helpful resource: https://www.derf.com/how-a-bridge-rectifier-works-step-by-step-tutorial/#:~:text=How%20does%20a%20Bridge%20Rectifier,of%20the%20input%20AC%20signal.
What is the Difference Between Half Bridge and Full Bridge Rectifier?
While both half bridge and full bridge rectifiers serve the common purpose of converting AC to DC, their configurations and applications differ. In a half bridge rectifier, only two diodes are used, conducting during alternate half-cycles of the AC waveform. In contrast, a full bridge rectifier employs four diodes, allowing for continuous DC output during both halves of the AC cycle. The full bridge configuration offers improved efficiency, reduced ripple, and enhanced control over the rectification process compared to its half bridge counterpart. Helpful resource: https://www.ccontrols.com/enews/2018/0518story2.htm#:~:text=A%20full%2Dwave%20rectifier%20device,for%20sharing%20the%20same%20transformer.
In conclusion: the Full Bridge Rectifier is a powerhouse in the realm of power electronics, efficiently converting alternating current into direct current with precision. Its robust design and ability to provide a steady and controlled DC output make it a go-to choice in various electronic applications. Understanding its working principles and the distinctions between full bridge and half bridge rectifiers empowers engineers and enthusiasts to make informed decisions in designing circuits for diverse power needs.
Facts Checked by Hugh Johnson
Hugh Johnson stands tall in the realms of both the chip industry and the electronic parts industry, earning acclaim as an esteemed expert in these fields. With an extensive background steeped in semiconductor technology, Hugh's expertise transcends chip design and fabrication, encompassing a profound understanding of electronic components' intricate functionalities and applications. His seasoned knowledge spans diverse facets, from microchip architecture and fabrication techniques to the broader landscape of electronic parts utilized across industries.









