TRIAC dimmers are among the most commonly used dimming devices in residential and commercial lighting systems. This guide will explore what TRIAC dimmers are, how they compare to other dimming technologies, and help you decide which dimming solution is best for your lighting needs.
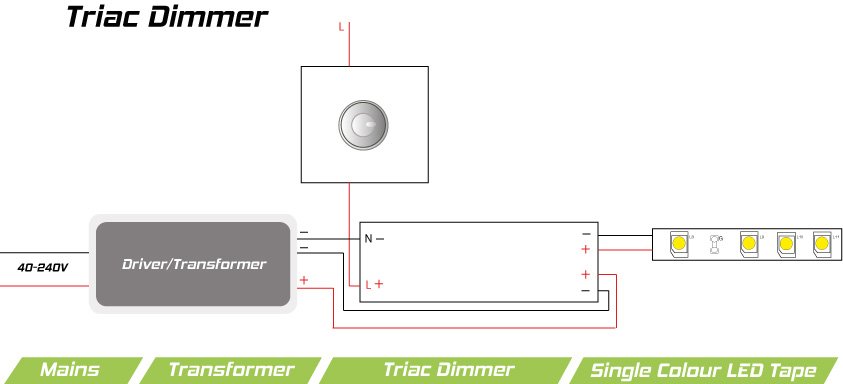
What are TRIAC Dimmers?
TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) dimmers are electronic devices used to adjust the brightness of incandescent, halogen, and some types of LED lights. They work by controlling the power delivered to the light bulb through phase-cutting, which chops part of the AC waveform, thereby reducing the average power sent to the light and dimming it.
What is the Difference Between a TRIAC Dimmer and a Regular Dimmer?
The term "regular dimmer" typically refers to the older resistive dimmers that worked by simply reducing the voltage supplied to the light, which was inefficient and often caused flickering. TRIAC dimmers, on the other hand, use a semiconductor switch to control the power more efficiently, leading to smoother dimming without flicker. TRIAC dimmers also work better with modern lighting technologies like LEDs, although compatibility still depends on the specific light bulb and dimmer model.
Is TRIAC Dimming the Same as ELV?
No, TRIAC dimming is not the same as ELV (Electronic Low Voltage) dimming. TRIAC dimmers are leading-edge dimmers, meaning they cut the leading edge of the AC waveform. ELV dimmers are trailing-edge dimmers, which cut the trailing edge of the waveform. ELV dimmers are generally used for electronic transformers and are preferred for dimming LEDs because they provide smoother operation with less noise and flickering.
Types of Dimmer Switches
There are several types of dimmer switches available, each with specific use cases:
- TRIAC Dimmers: Leading-edge dimmers commonly used with incandescent, halogen, and some LED lights.
- ELV (Electronic Low Voltage) Dimmers: Trailing-edge dimmers used for LEDs and electronic transformers.
- 0-10V Dimmers: Typically used in commercial applications, offering precise control over fluorescent and LED lights.
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Dimmers: Used for LEDs, controlling the brightness by rapidly switching the light on and off.
- Smart Dimmers: Integrated with home automation systems, allowing control via apps or voice commands.
How Does a TRIAC Dimmer Work?
A TRIAC dimmer works by chopping the AC waveform. When you adjust the dimmer, you are essentially controlling the point in the AC cycle where the TRIAC begins conducting. By delaying the conduction point, less power is delivered to the light, resulting in a dimming effect. The TRIAC switches off at the end of each half-cycle, and the process repeats with the next cycle.
Pros and Cons of a TRIAC Dimmer
Pros:
- Compatibility: Works with many types of lights, including incandescent and some LEDs.
- Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper than other dimming technologies.
- Simplicity: Easy to install and use.
Cons:
- Compatibility Issues: Not all LEDs are compatible with TRIAC dimmers, which can result in flickering.
- Electrical Noise: Can generate electrical noise, leading to interference with other devices.
- Heat: Can generate heat, especially at lower dimming levels.
Consumer Grade Dimming Solutions – TRIAC vs. PWM vs. 0-10v
When choosing a dimming solution, it’s important to consider the type of lighting and the desired dimming performance:
- TRIAC Dimmers: Best for incandescent, halogen, and some LEDs. Cost-effective but may cause flickering with some LEDs.
- PWM Dimmers: Ideal for LED lights, offering precise control with minimal flicker. More complex and can be more expensive.
- 0-10V Dimmers: Common in commercial settings, providing smooth and consistent dimming. Requires compatible fixtures and more complex wiring.
Industrial Grade Alternatives to TRIAC Dimmer
In industrial settings, more robust dimming solutions are often required:
- Digital Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI): Provides precise control over large lighting installations with digital communication between dimmers and fixtures.
- Phase-Adaptive Dimmers: Automatically adjust between leading-edge and trailing-edge dimming, ensuring compatibility with various light types.
- DMX Dimmers: Used in theatrical and architectural lighting for precise control over complex lighting setups.
Which Dimming Solution Is Best for Your Lights?
The best dimming solution depends on your specific needs:
- For Residential Use: TRIAC dimmers are a good choice for compatibility and cost-effectiveness with traditional light bulbs.
- For LED Lighting: Consider PWM or ELV dimmers to avoid flickering and ensure smooth dimming.
- For Commercial or Industrial Applications: 0-10V, DALI, or phase-adaptive dimmers provide the flexibility and control needed for large-scale lighting systems.
Choosing the right dimmer ensures not only the best performance of your lighting system but also extends the lifespan of your lights, improving both efficiency and user experience.
Facts Checked by Hugh Johnson
Hugh Johnson stands tall in the realms of both the Integrated Circuits (ic Chips) industry and the electronic parts industry, earning acclaim as an esteemed expert in these fields. With an extensive background steeped in semiconductor technology, Hugh's expertise transcends chip design and fabrication, encompassing a profound understanding of electronic components' intricate functionalities and applications. His seasoned knowledge spans diverse facets, from microchip architecture and fabrication techniques to the broader landscape of electronic parts utilized across industries.









